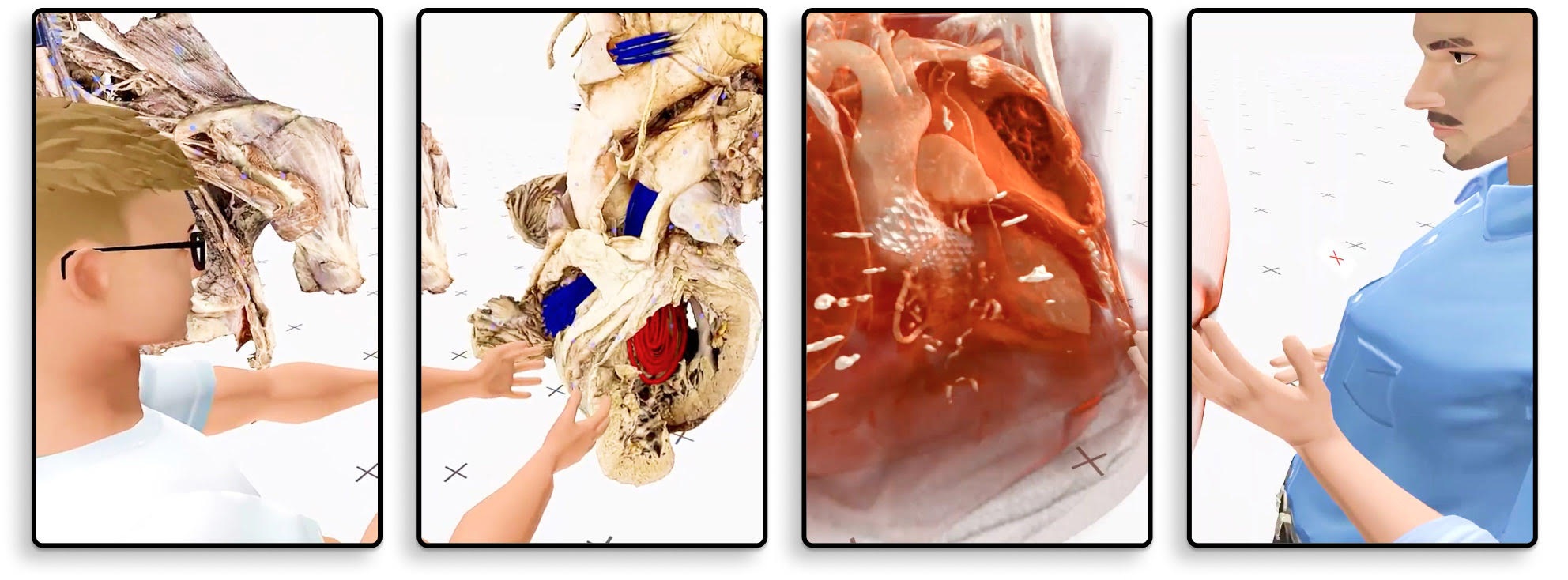
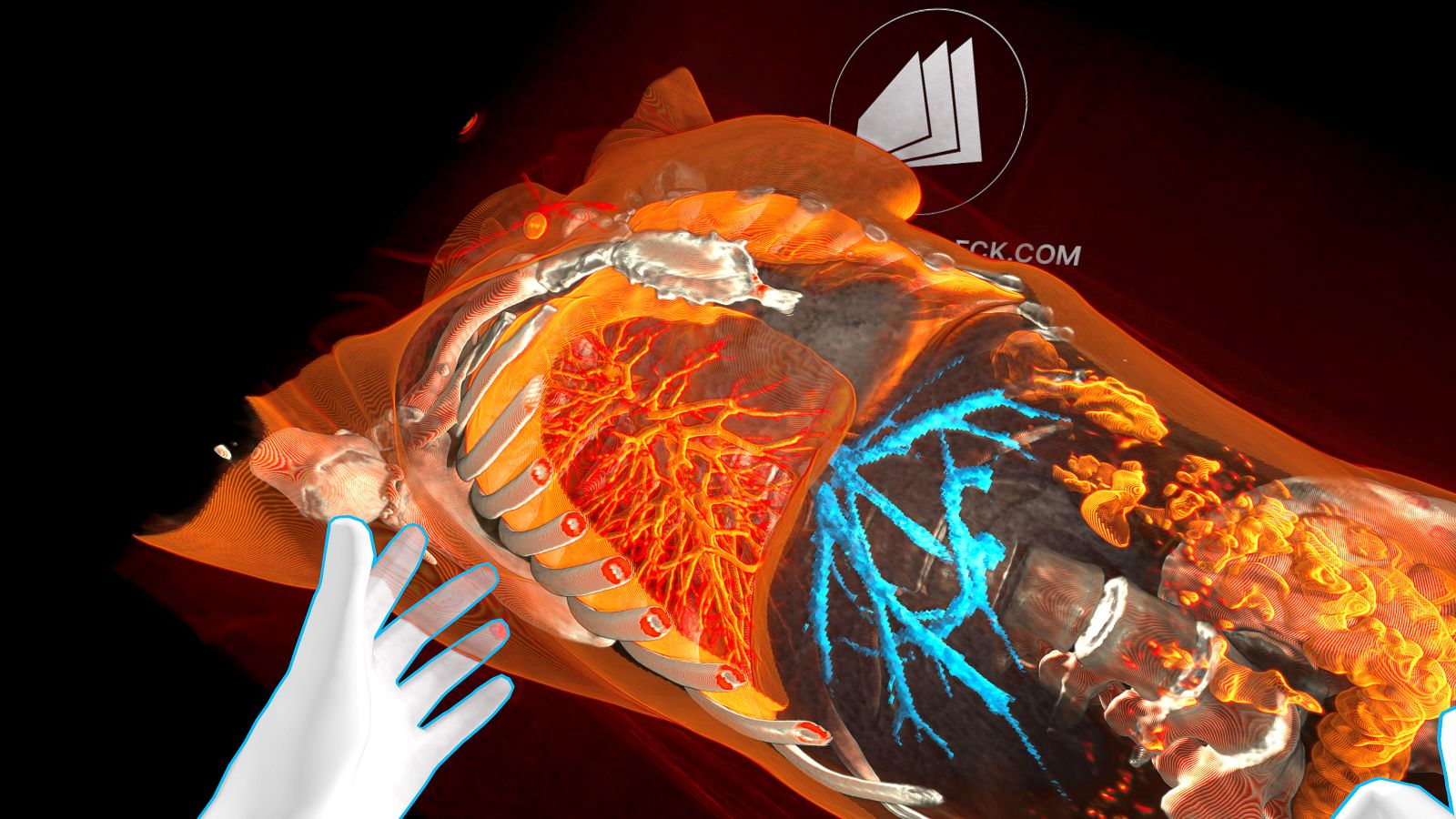
Picking Up a Controller Before a Scalpel
Transforming Spinal Surgery Through Medical VR
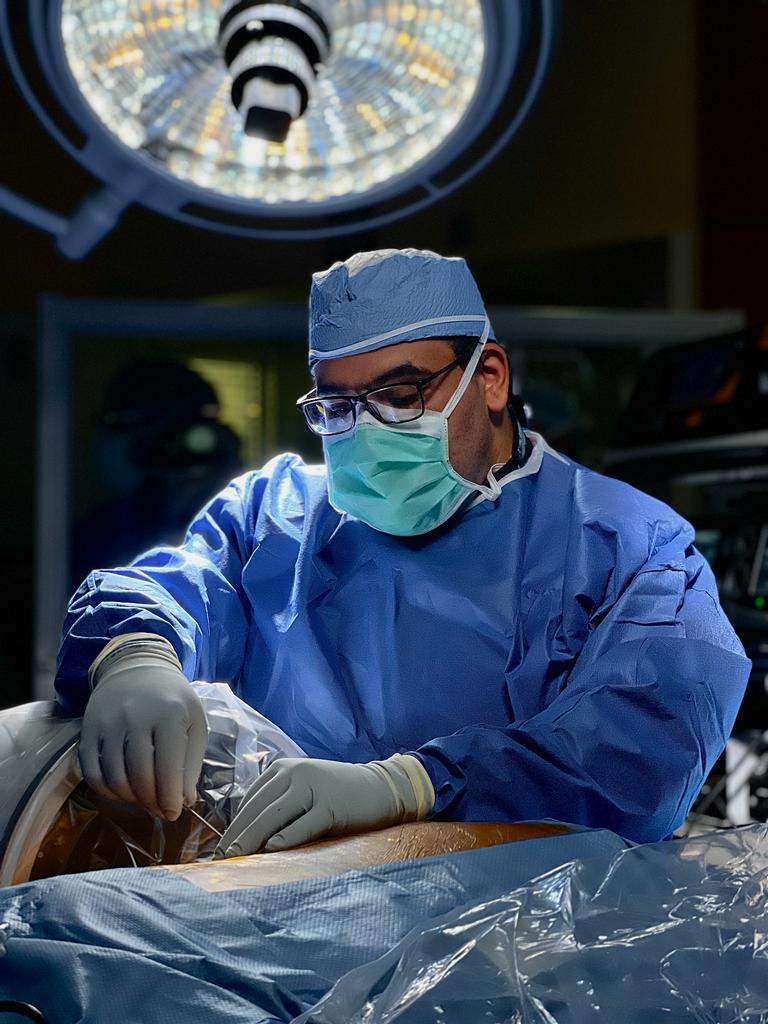
Galal Elsayed, M.D. during an ultraminimally invasive endoscopic spinal approach for discectomy. Photo by Ryan Moody | © Galal Elsayed 2023
Spatial Computing is revolutionizing spine surgery by providing interactive, four-dimensional models of patient anatomy, enhancing surgeons' understanding and planning. This case report by Galal A. Elsayed and his team emphasizes SC's significant impact on preoperative planning and postoperative evaluation in spinal revision surgery, underscoring its ability to improve surgical precision and patient outcomes.
Elsayed GA, Lavadi RS, Pugazenthi S, Jaikumar V, Mitha R, Hafez DM, Ogunlade JO, Agarwal N. Spatial Computing for preoperative planning and postoperative evaluation of single-position lateral approaches in spinal revision surgery. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2023 Apr-Jun;14(2):208-211. doi: 10.4103/jcvjs.jcvjs_48_23. Epub 2023 Jun 13. PMID: 37448505; PMCID: PMC10336895. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10336895/
Case Overview: A Complex Spinal Challenge
The subject of this case report is a 79-year-old male, wheelchair-bound due to chronic lumbar pain and bilateral lower extremity weakness. His medical history reveals a previous L2-L5 lumbar decompression with posterior fixation. Further examination and imaging revealed thoracic myelopathy, pseudoarthrosis, and cord compression, necessitating a comprehensive surgical intervention. This case underscores the complexities inherent in spinal revision surgeries and the critical need for precise preoperative planning and postoperative evaluation.
The Role of Spatial Computing in Surgical Planning
The introduction of spatial computing into the surgical planning phase allowed for an in-depth analysis of the patient's spinal condition. By exporting the patient's imaging into a spatial computing environment, the surgical team could assess the pseudoarthrosis at L2-3 and L4-5 and plan a two-staged operation to address the multiple spinal issues effectively. The spatial computing environment facilitated the visualization of critical anatomical structures, aiding in the decision-making process for the surgical approach, graft sizing, and trajectory planning. This level of detail provided by spatial computing is instrumental in devising a tailored surgical plan that addresses the patient's specific needs.
Surgical Procedure and Outcomes
Following the spatial computing-assisted preoperative planning, the patient underwent a successful two-staged spinal revision surgery. The procedure involved decompression to relieve spinal cord compression, followed by lateral lumbar interbody fixation and anterior lumbar interbody fixation, with the placement of cobalt-chromium rods for stabilization. The postoperative period was uneventful, and the patient showed significant improvement, highlighting the efficacy of spatial computing in enhancing surgical precision and patient outcomes.
The Advantages of Spatial Computing
This case report illuminates the multifaceted advantages of spatial computing in spinal revision surgery. By enabling a three-dimensional, interactive exploration of the patient's anatomy, spatial computing enhances the surgeon's familiarity with the specific surgical landscape. This increased anatomical awareness is crucial for minimizing the risks associated with complex spinal surgeries and ensuring optimal placement of internal fixation devices. The case also points to the potential of spatial computing in evaluating postoperative outcomes, offering a comprehensive view of the surgical corrections and their alignment with the preoperative plan.
Towards a New Standard in Spine Surgery
The successful application of spatial computing in this spinal revision surgery case sets a precedent for the integration of advanced technological tools in surgical planning and evaluation. As spatial computing becomes more commonplace, it promises to propel the field of spine surgery into a new era of precision and patient-specific care. This case report by Elsayed and colleagues not only demonstrates the immediate benefits of spatial computing but also opens the door to future innovations in surgical approaches to spinal pathologies.
For more information, contact info@medicalholodeck.com August 2023